Example Graphs
GDN comes with a set of easily graspable graphs that are used to demonstrate the APIs.
You can use the add samples tab in the create graph window in the web interface and use it to create instances of these graphs in your GDN fabric. Once you've created them, you can them in GUI.
The Knows_Graph
A set of persons knowing each other:
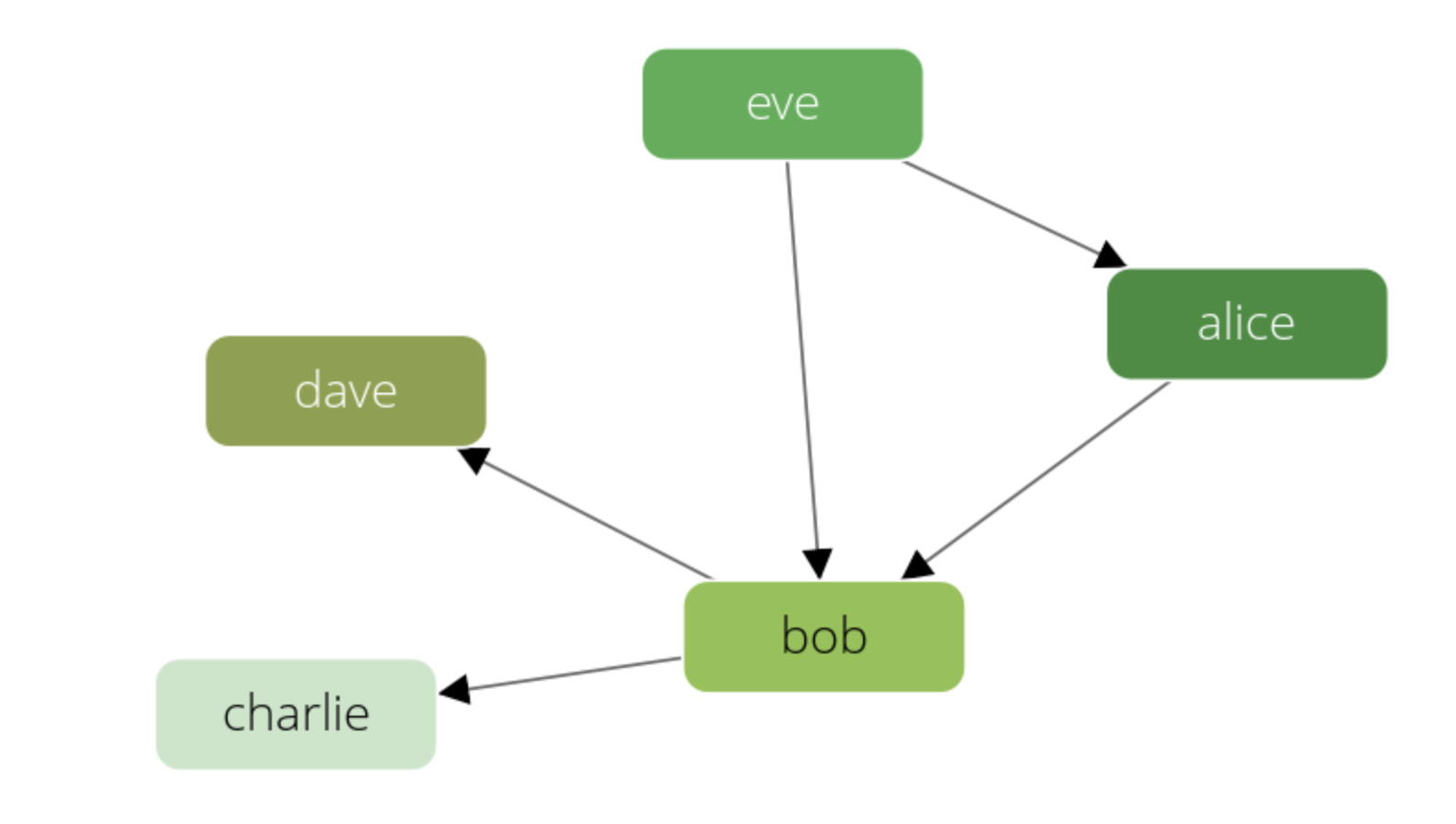
The knows graph consists of one vertex collection persons connected via one edge collection knows.
It will contain five persons Alice, Bob, Charlie, Dave and Eve.
We will have the following directed relations:
- Alice knows Bob
- Bob knows Charlie
- Bob knows Dave
- Eve knows Alice
- Eve knows Bob
With the default "Search Depth" of 2 of the graph viewer you may not see all edges of this graph.
The Social Graph
A set of persons and their relations:
This example has female and male persons as vertices in two vertex collections - female and male. The edges are their connections in the relation edge collection.
The City Graph
A set of european cities, and their fictional traveling distances as connections:
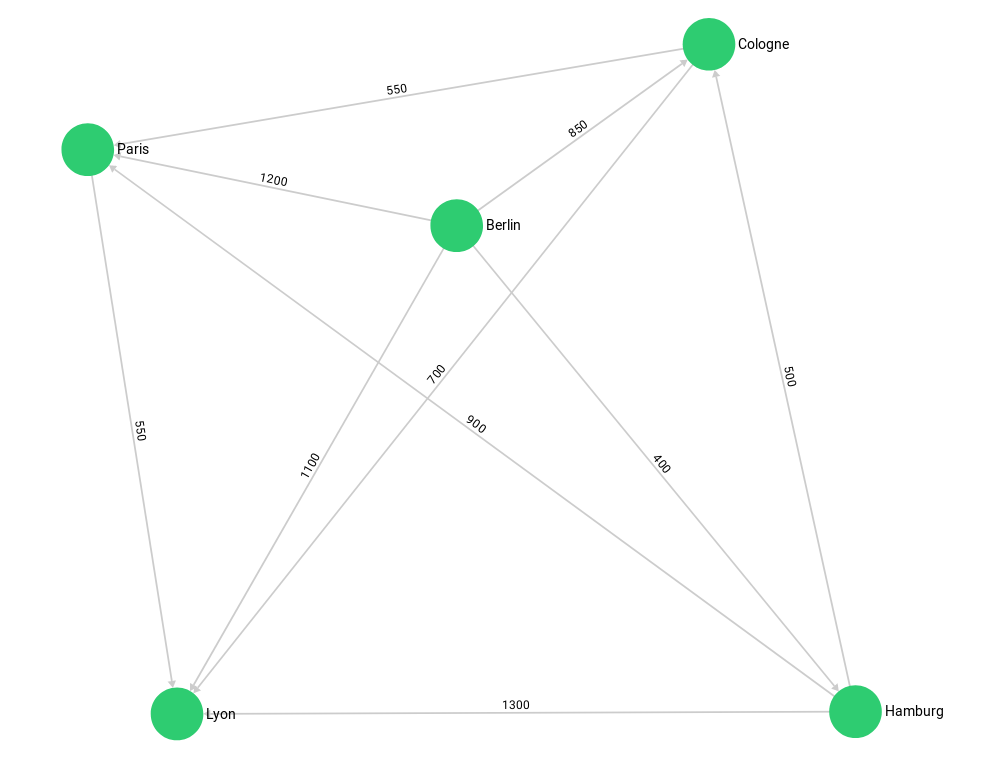
The example has the cities as vertices in several vertex collections - germanCity and frenchCity. The edges are their interconnections in several edge collections french / german / international Highway.
The Traversal Graph
This graph was designed to demonstrate filters in traversals. It has some labels to filter on it.
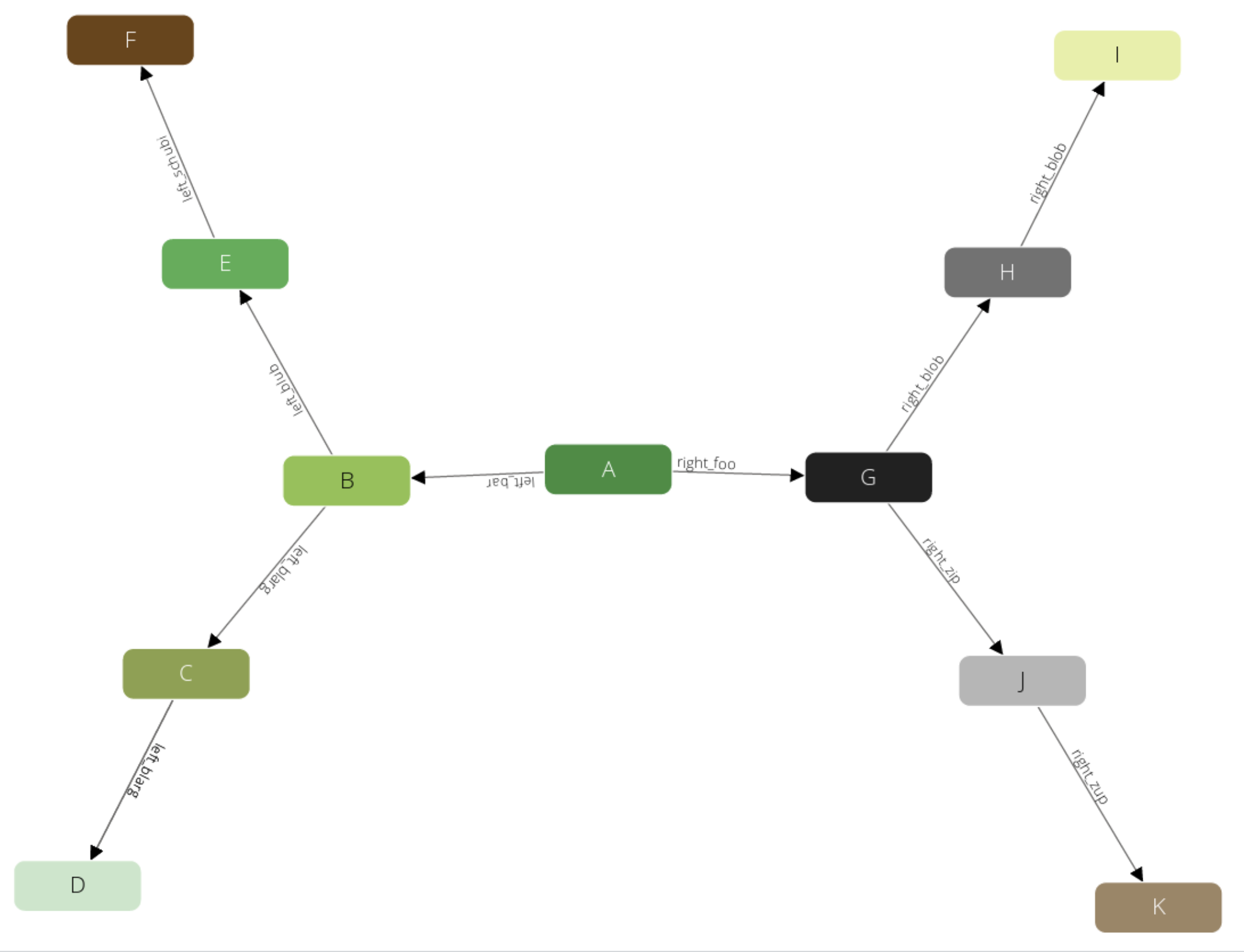
The example has all its vertices in the circles collection, and an edges edge collection to connect them.
Circles have unique numeric labels. Edges have two boolean attributes (theFalse always being false, theTruth always being true) and a label sorting B - D to the left side, G - K to the right side. Left and right side split into Paths - at B and G which are each direct neighbors of the root-node A. Starting from A the graph has a depth of 3 on all its paths.
With the default "Search Depth" of 2 of the graph viewer you may not see all nodes of this graph.
The k Shortest Paths Graph
The vertices in this graph are train stations of cities in Europe and North America and the edges represent train connections between them, with the travel time for both directions as edge weight.
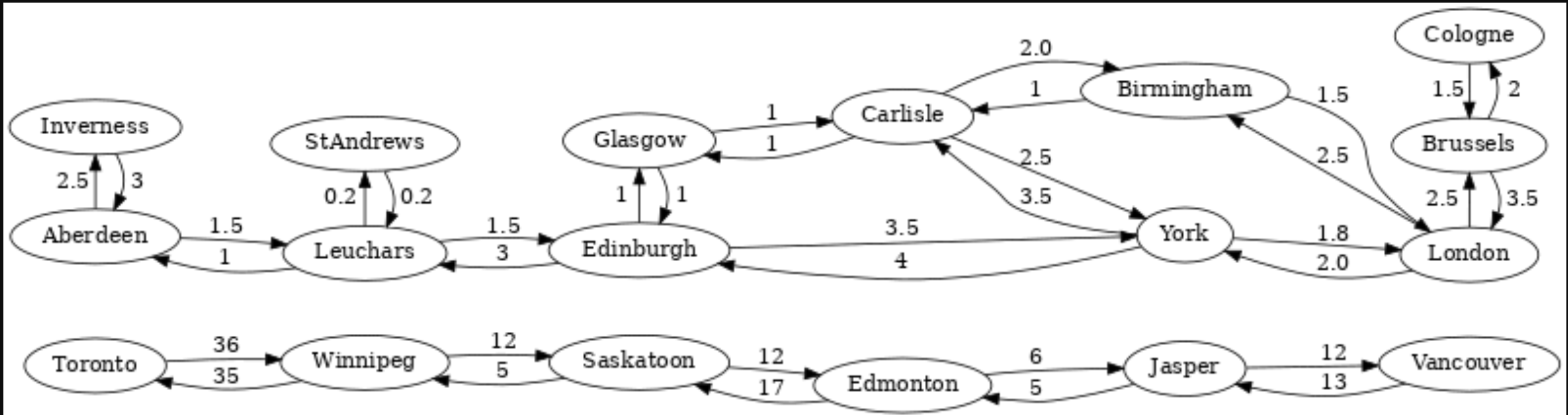
See the Shortest Paths page for query examples.
The World Graph
The world country graph structures its nodes like that: world → continent → country → capital. In some cases edge directions aren't forward (therefore it will be displayed disjunct in the graph viewer). It has two ways of creating it. One using the named graph utilities (worldCountry), one without (worldCountryUnManaged).
It is used to demonstrate raw traversal operations.
The Mps Graph
This graph was created to demonstrate a use case of the shortest path algorithm. Even though the algorithm can only determine one shortest path, it is possible to return multiple shortest paths with two separate queries. Therefore the graph is named after the multiple path search use case.
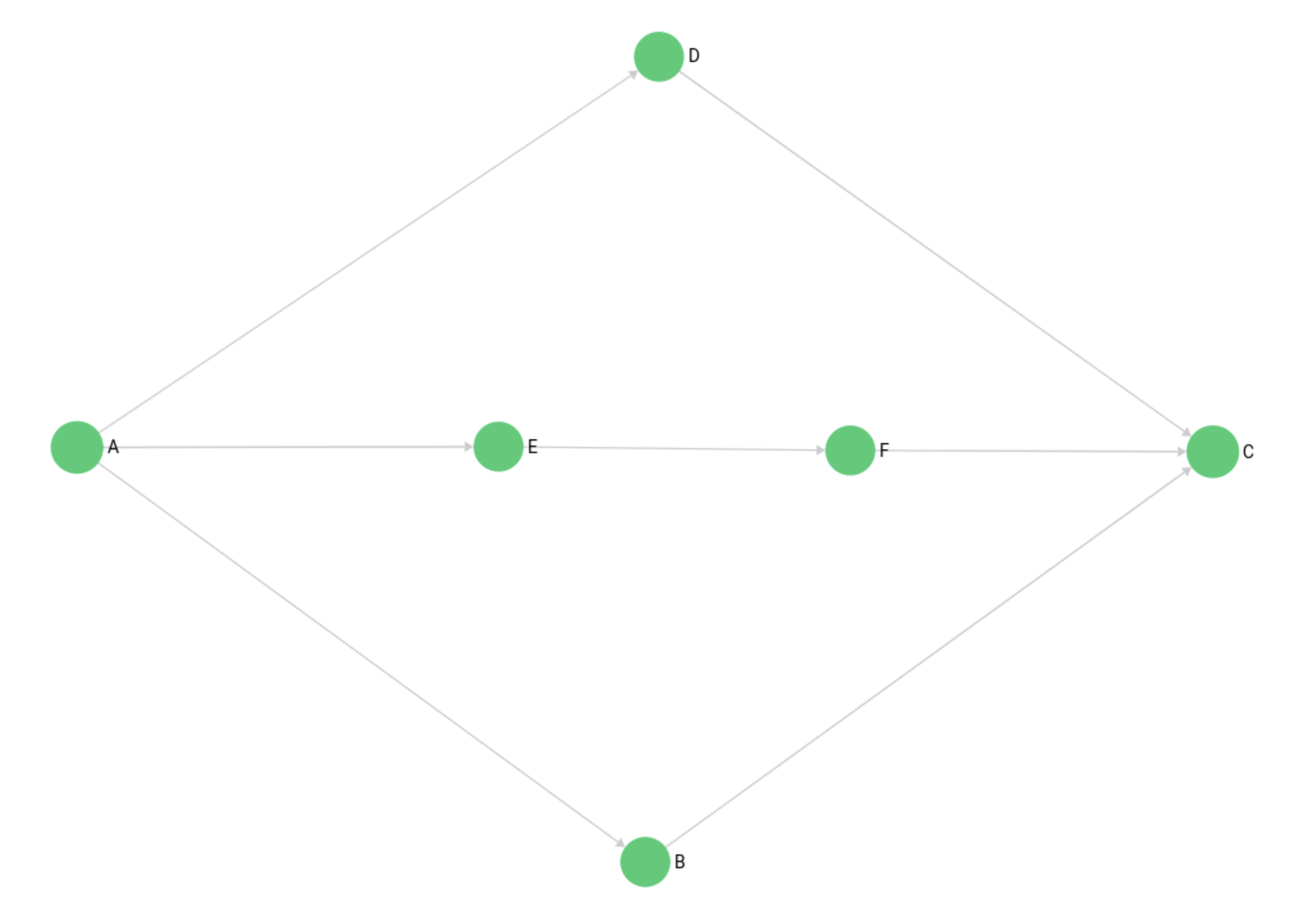
The example graph consists of vertices in the mps_verts collection and edges in the mps_edges collection. It is a simple traversal graph with start node A and end node C.
Higher volume graph examples
All of the above examples are rather small so they are easier to comprehend and can demonstrate the way the functionality works. Example: Pokec social network