Stream Workers
Macrometa GDN allows you to integrate streaming data and take appropriate actions. Most stream processing use cases involve collecting, analyzing, and integrating or acting on data generated during business activities by various sources.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Collect | Receive or capture data from various data sources. |
| Analyze | Analyze data to identify interesting patterns and extract information. |
| Act | Take actions based on the findings. For example, running simple code, calling an external service, or triggering a complex integration. |
| Integrate | Provide processed data for consumer consumption. |
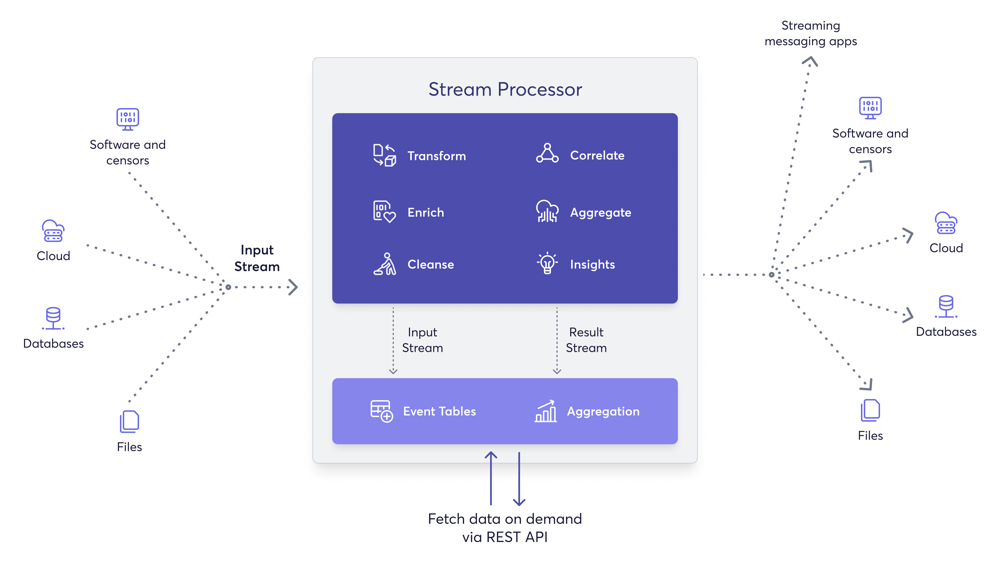
You can process streams to perform the following actions with your data:
- Transform data from one format to another. For example, from XML to JSON.
- Enrich data received from a specific source by combining it with databases and services.
- Correlate data by joining multiple streams to create an aggregate stream.
- Clean data by filtering it and by modifying the content in messages. For example, obfuscating sensitive information.
- Derive insights by identifying event patterns in data streams.
- Summarize data with time windows and incremental aggregations.
- Extract, transform, and load (ETL) collections, tailing files, and scraping HTTP endpoints.
- Integrating stream data and trigger actions based on the data. This can be a single service request or a complex enterprise integration flow.
Architecture
The architecture of Macrometa stream processing engine fits this natural flow. Following are the major components of our stream processing engine.
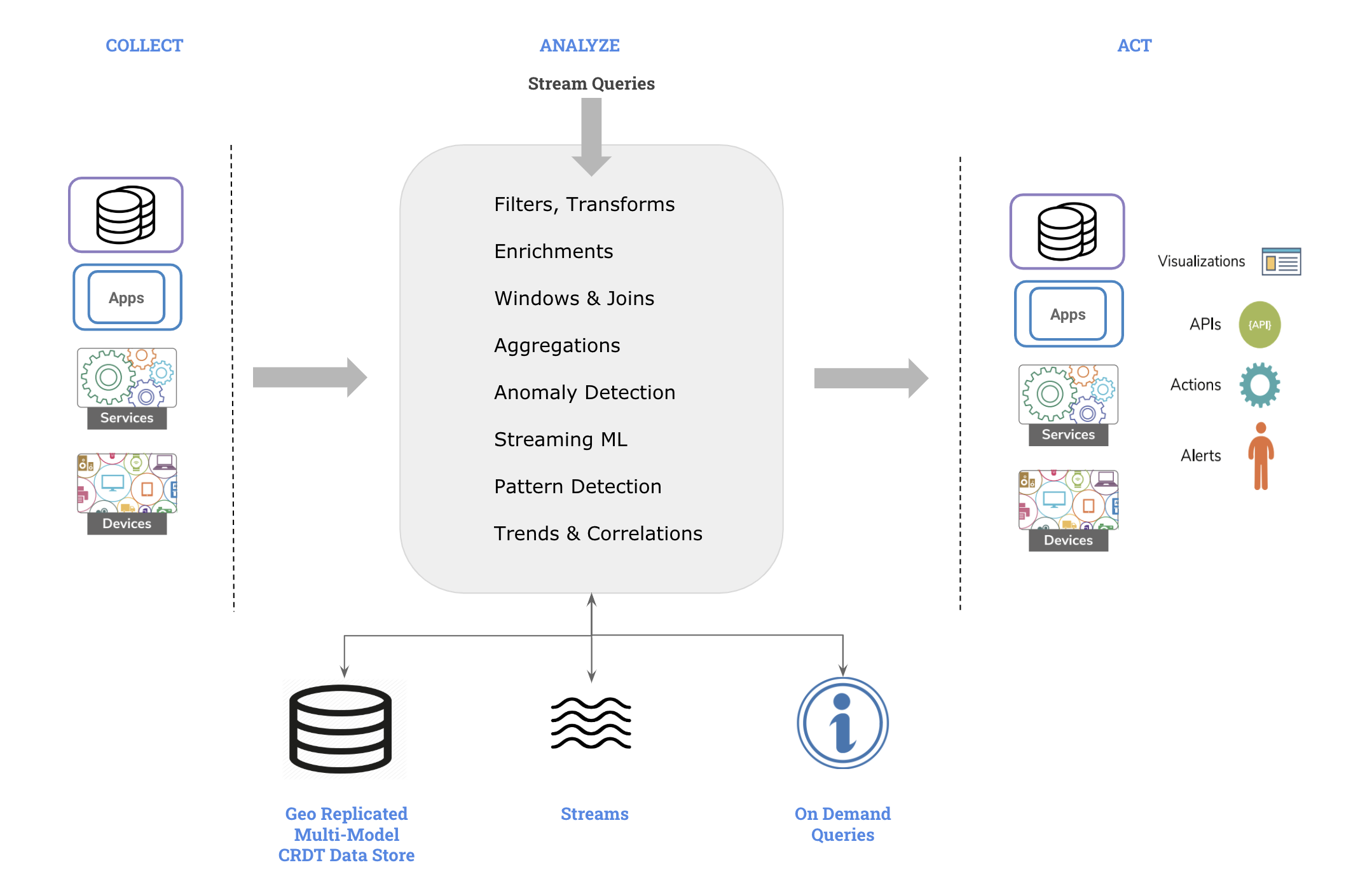
The stream processing engine receives data event-by-event and processes them in real-time to produce meaningful information i.e.,
- Accept event inputs from many different types of sources.
- Process them to transform, enrich, and generate insights.
- Publish them to multiple types of sinks.
To use stream processor, you need to write the processing logic as a stream application using streaming SQL language which is discussed in the Stream Query Guide.
When the stream application is published, it:
- Consumes data one-by-one as events.
- Pipe the events to queries through various streams for processing.
- Generates new events based on the processing done at the queries.
- Finally, sends newly generated events through output to streams.
Key Features
Macrometa stream processing engine allows you to write rich & complex stream processing logic using an intuitive SQL-like language. You can perform the following actions on the fly using stream queries and constructs.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Realtime ETL | In realtime, extract data when available, transform it on the fly, and integrate it using sinks (http, streams, mqtt..) etc. |
| Consume & Publish Events | Consume and Publish events via Kafka, HTTP, TCP, MQTT, Amazon SQS, Google Pub/Sub, WebSocket, S3 and Google Cloud Storage |
| Data Filtering | Filter events based on conditions such as value ranges, string matching, regex, and others. |
| Data Cleansing | Filter out corrupted, inaccurate or irrelevant data from a data stream based on one or more conditions. Modify or replace content to hide/remove unwanted data parts from a message (e.g., obscuring). Clean data by setting defaults, and handling nulls, using default, if-then-else functions, and many others. |
| Data Transformations | Support data extraction and reconstruction of messages using inline mathematical and logical operations, inbuilt functions and custom functions in JavaScript for processing JSON, string, time, math, regex, and others. |
| Data Enrichment | Enrich the data received in the stream with data from c8db or another data stream, or an external service to derive an expected result |
| Data Summarization | Aggregate data using sum, count, average (avg), min, max, distinctCount, and standard deviation (StdDev) operators. Summarize events based on time intervals like sliding time, tumbling/batch time windows and based on number of events like sliding length, and tumbling/batch length windows. Support for data summarization based on sessions and uniqueness. Support for named aggregation and aggregation of data based on group by fields, having conditions. Sort & limit the aggregated output using order by and limit keywords. |
| Scripting | Write custom functions in JavaScript and use within streaming queries. |
| Pattern & Trend Mining | Identifies event occurrence patterns among streams over time. Identify non occurrence of events. Supports repetitive matches of event pattern occurrences with logical conditions and time bound. |
| Sequence Processing | Identifies continuous sequence of events from streams. Supports zero to many, one to many, and zero to one event matching conditions. |
| Scatter-Gather | Process complex messages by dividing them into simple messages using tokenize function, process or transform them in isolation, and group them back using the batch window and group aggregation. Ability to modularize the execution logic of each use case to build a composite event-driven applications. Provide execution isolation and parallel processing by partitioning the events using keys or value ranges. |
| Data Pipelines | Periodically trigger data pipelines based on time intervals, and cron expression using triggers. Support for calling HTTPservices in a non-blocking manner to fetch data and enrich events. Handle responses accordingly for different response status codes. Divert the events to error stream to handle the errors gracefully. |
| Geo Replicated Data Store | Query, modify, and join the data stored in tables which support primary key constraints and indexing. |
| Rule Processing | Execution of rules based on single event using filter operator, if-then-else and match functions, and many others. Rules based on collection of events using data summarization, and joins with streams, tables, windows or aggregations. Rules to detect event occurrence patterns, trends, or non-occurrence of a critical events using complex event processing constructs such as pattern, and sequence. |
| Realtime Decisions as Service | Provide REST APIs to query multi-modal geo-replicated tables, windows and named-aggregations to make decisions based on the state of the system. |
These features allows you to build robust global data processing and integration pipelines at the edge by combining powerful stream processing, multi-model database and geo-replicated streams capabilities.